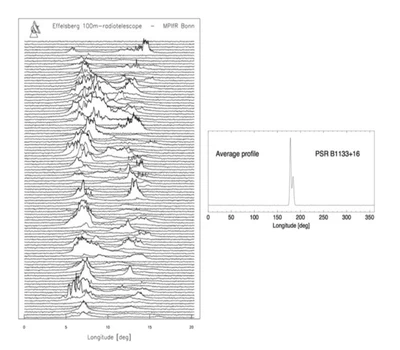
The Pulsars were discovered by Jocelyn Bell in 1967 and have been studied extensively by the scientific community using huge-size radiotelescopes.
They are neutron stars with ultra-fast spinning, and their rotation speed can be very precise, leading to a new category of oscillators that remain stable over hundreds of thousands of years. “Pulsar” is an abbreviation for “PULSAting Radio source”: these celestial bodies emit a powerful radio-electromagnetic beam that behaves like a beacon in the sky when crossing the observer’s path.
However, these signals are very faint due to the observed distances and are challenging to observe. Today, they are utilized for measuring low-frequency gravitational waves in what is known as a Pulsar Timing Array (PTA).
At PulSR our mission is to build an industrial, flat and compact-size phased-array radiotelescope capable of receiving and processing pulsar signals, in order to bring to the industry a novel and alternative source to improve the resiliency of PNT systems.
Our technology is based on iterations on an innovative L-Band aperture array radiotelescope, adapted to pulsar observations (White paper available under request).
Based in Lyon (France), PulSR was founded in 2022 by an experienced team :
- Alexis Rigaud - CEO & CTO - R&D Engineer
- Julien Lambert - CSO - Astrophysicist
- Nicolas George - Counsel & CFO - MBA
We are at pre-seed stage and currently developping the prototype.